Adding custom middleware in Dot Net Core application
Introduction
In ASP.NET Core, middleware plays a crucial role in request
processing pipelines, acting as a conduit through which HTTP requests flow
before reaching the destination.
By integrating a custom middleware class into your
application, you gain the flexibility to intercept, modify, or handle requests
and responses according to your specific requirements. This powerful feature
allows developers to inject custom logic at various stages of request
processing, thereby enhancing functionality, improving security, and optimizing
performance.
This introduction will guide you through the process of
implementing custom middleware in the Program.cs file of a .NET Core
application, showcasing practical examples and best practices.
Steps of adding the custom middleware
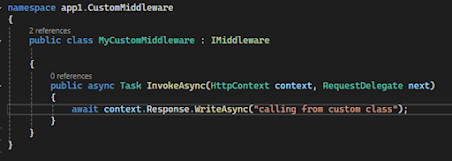
Create a Custom Middleware Class:
- Create
a new class file, for example MyCustomMiddleware.cs.
Inherit
the class with an interface IMiddleware and implement the
interface’s methods.
·
Change the code of the method InvokeAsync
with the custom code
Note: The MyCustomMiddleware in
this example is inside a folder named ‘CustomMiddleWare’ hence the namespace is
showing as app1.CustomMiddleWare (my application name is app1)
Adding the custom middleware in the pipeline:
·
Add the namespace in Program.cs
·
Add the custom middleware class using
AddTransient method just after the var builder line as shown below:
Note : the line of adding the custom middleware should be before the
builder.Build() command.
·
In order to call the custom middleware class,
add a line
app.UseMiddleware<MyCustomMiddleware>();
Conclusion
By incorporating custom middleware into your ASP.NET Core
application, you harness the power to tailor the request-handling pipeline to
your specific requirements. This enables you to inject custom logic, enhance
security measures, and optimize performance throughout the request-processing
flow.
The modular nature of
middleware promotes cleaner code and better maintainability, allowing for the
seamless addition of new functionality without disrupting existing components.
By understanding and utilizing custom middleware, developers can build more
robust, flexible, and efficient applications, ultimately delivering superior
user experience. Happy coding!